Common name: Cucumber/Pumpkin family
Number of genera: This family includes 110 genera and about 640 species
Propagation type: Fruit or seed
Distribution: The species of this family are distributed throughout the world. In India this family is represented by about 37 genera and 97 species distributed throughout the country. The chief centre of distribution of these members is Eastern Himalayas.

Habitat: Members of this family are mostly mesophytes and some xerophytes are also known to exist in this family.
Habit: The plants are mostly succulent, trailing, decumbent annual or perennial herbs. These plants climb by means of laterally spirally coiled, simple or branched tendrils.
Root system: These plants have woody tap root system.
Stem: The stem is usually herbaceous, branched, hairy and five angular with two alternate rings of five vascular bundles each.
Leaf: The leaves are simple, alternate, exstipulate, long petioled, and frequently cordate. The leaves are often palmately or pinnately lobed. The petioles are often hollow and stipules are absent
Inflorescence: Inflorescence is cymose type. It may be axillary and bears a solitary female flower. The male flowers may be solitary or in the form of racemes, corymbs or panicles. The plants are monoecious or sometimes dioecious as in Coccinia cordifolia and Mimordica dioca.
Flower: The flowers are yellow or white, unisexual (rarely bisexual), actinomorphic, pentamerous and epigynous (rarely perigynous as in Actinostemma). The thalamus forms a cup above the ovary.

Calyx: The calyx is of 5 sepals forming a tube, which is wholly adnate to the ovary in female flowers. The aestivation is imbricate or valvate.
Corolla: The corolla consists of 5 petals which are united to form a tube or nearly free (Trichosanthes). The corolla is campanulate (Coccinia, Cucurbita), rotate or salver form. The lobes are imbricate or induplicate valvate. Petals are white or yellow in color. The petals are free in Luffa, Trichosanthes.
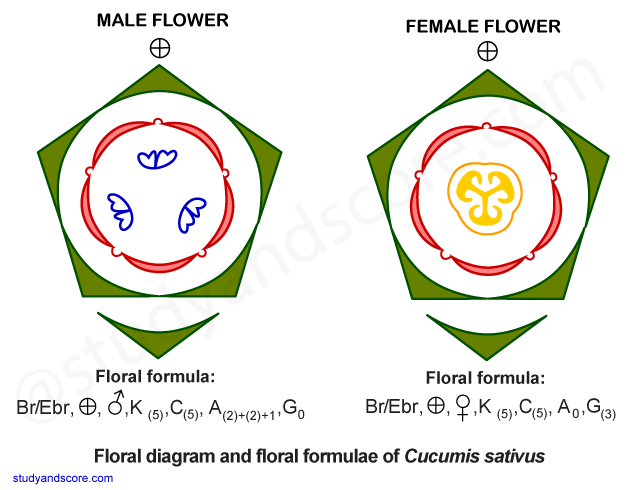
Androecium: The Androecium is present in the male flowers only. In female flowers it may be represented by staminodes. The Androecium shows much variation. The simplest condition is where 5 free stamens are present (Fevillea, Luffa cylindrica) with dithecous/monothecous anthers.
Thladiantha has five stamens with monothecous anthers; the filaments of four stamens are coherent at the base into two pairs, whereas the fifth stamen stands apart.
In Lagenaria, Cucumis and Citrullus there are three stamens with one monothecous anther and other two as dithecous anthers.
In Cucurbita there are three stamens with twisted anthers and connate filaments
In Sicyos the filaments of all stamens are united into a column bearing the curved anthers
In Cyclanthera the stamens are united into a column with two ring-like pollen chambers running around the top. Here the anthers dehisce through a single longitudinal slit.

Gynoecium: The gynoecium is present only in the female flowers. It consists of 3 syncarpous carpels with completely inferior or half-inferior ovary. The ovary is unilocular with three intruding and bifurcating placentae which often meet at the center. Thus, ovary becomes spuriously three loculed. Ovary consists of many anatropous ovules in the placenta. They have only one style with three stigmas.

Pollination: The members of this family are mostly bee pollinated and often they need to be hand pollinated. The flowers are small, green and inconspicuous. The flowers may be visited by insects for nectar which is secreted by a cup shaped disc in male and female flowers.
When an insect in search of honey inserts its proboscis, then its head is covered by the stamens and gets sprinkled with the pollen. This same insect may visit and transfer the pollen on to the female flower.
Fruit: The fruit is fleshy-berry with soft or hard pericarp. This type of fruit is called pepo. It is usually indehiscent, but rarely dehiscent in Mimordica. The shape and size of the fruit varies considerable in various species.

Seed: The seeds are compressed and non-endospermic with straight embryo. The seeds have large and leafy cotyledons. They are dispersed by explosive opening of the fruit. Viviparous germination is seed Sechium.
The following is a list of some important members of family cucurbitaceae, arranged alphabetically.
Hope you have liked this post.
Please share it with your friends through below links.
All the very best from Team Studyandscore
“Study well, Score more…”
- Share with your friends! -
Login to post your comment here...
- or with social Account -